660530075688
HBMT2103
ASSIGNMENT QUESTION
Misconception on capacity may arise among the students while teaching Volume of liquid especially when comparing capacity of two containers that can hold more. Students often make the comparison on height rather than its capacity. Find ONE (1) video in the internet that show how volume of liquid are measured. Create TWO (2) teaching aids that can be applied to Year Two students to help them understand better. Based on your teaching aids, you are required to create TWO (2) teaching activities; each for high achiever and low achiever students. Finally, you are required to develop your own blog and post the video, teaching aid and teaching activities in your blog. You are free to choose any platforms that are available in the internet. For reference you may browse at www.blogger.com on developing your blog. You are only required to submit link to your blog.
Introduction
Measuring is one of the topics in KBSR mathematics that we use most because it has many practical applications in our real life situations. There are many mathematical concepts and procedures that underlie both measurement and number concepts. Measurement provides an excellent way to present problem-solving experiences at every level of KBSR mathematics. Just like in other subjects, students have misconceptions in mathematics. These misconceptions are derived from their prior knowledge and experiences with numbers in their everyday lives. These misconceptions hinder the learning process, because they are tightly held by students. So,teachers need to provide tangible experiences to break these misconceptions. Recognizing student misconceptions and immediately focusing a discussion on the misconception is important. Providing guiding questions using inductive reasoning is the best approach. One of the misconceptions in Mathematics is “The Tallest Container Always has the Greatest Volume”. According to conventional wisdom, children below a certain age lack the concept of the conservation of liquid volume. Children often believe that the amount of liquid has changed when a set amount has been poured from one container to another of a different size. They believe that there is more liquid in the one that has the highest level.
Video
Teaching aid (1)
Teaching aid (1)
| Low Achiever students | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Activity 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
- Learning Outcome:
- To compare volume of liquid.
Materials:
- Different size of clear containers
- Measuring cylinders (Marked A,B,C and D)
- A few bags of coloured-water (each bag contains the equal volume of coloured-water)
Procedures
1. Divide the class into groups of six and have them work in their cooperative groups.
2. Appoint one of the group members as the recorder.
3. Give each group a set of different size of clear containers, four measuring cylinders and four
bags of coloured-water.
bags of coloured-water.
4. Have the students to fill each container with a bag of coloured-water each.
5. The students will have to arrange the containers in ascending order according to the level of
coloured-water in the container.
coloured-water in the container.
6. The recorder records the answer.
Expected answer: A, C, D, B
Expected answer: A, C, D, B
7. Ask the students to pour the coloured-water of each container into a measuring cylinder
each.
each.
8. Have the students to compare the volume of water in the containers.
9. The students are asked to compare the height of water level in the containers. They should be equal.
10. Have the students to say
(i) Container A holds the same amount of coloured-water as container B.
(ii) Container B holds the same amount of coloured-water as container C.
(iii) Container C holds the same amount of coloured-water as container D.
11. Conclusion
All the containers have the same volume of water.
11. Conclusion
All the containers have the same volume of water.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Worksheet Name : ___________________________ Date :
Year 2 ____
Cicle the container that holds less water
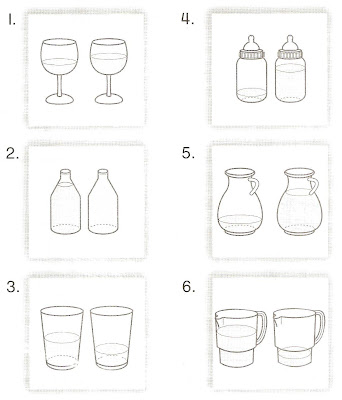
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
High achiever students
High achiever students
Activity 2
Learning Outcome:
- To compare volume of liquid.using standard measurement
- To measure the volumes of liquid.
Materials:
- Different sizes of clear containers
- 500ml graduated beakers (marked A,B, C, D, E and F )
- A jug of coloured-water
Prosedures
1. Divide the class into groups of four and have them work in their cooperative groups.
2. Appoint one of the group members as the recorder.
3 Give each group a set of different sizes of clear containers with six beakers.
5. The students will have to arrange the containers in ascending order according to the level of
water in the containers.
water in the containers.
6. The students are asked to determine whether each containers has the same volume, or
whether has more. The recorder records their answer.
whether has more. The recorder records their answer.
7. The students pour water from container A to beaker A, container B to beaker B, container
C to beaker C and etc
8. Students read the measurements and complete the table below.
C to beaker C and etc
8. Students read the measurements and complete the table below.
Container | A | B | C | D | E | F |
Volume (ml) | 300ml | 150ml | 200ml | 150ml | 300ml | 200ml |
Teaching aid (2)
Picture A
Low achiever students
Low achiever students
Activity 1:
Learning Outcome:
- To compare volumes of liquid.
- 500ml graduated beakers
- Various clear containers of different sizes
- A jug of coloured-water
1. Divide the class into five groups.
2. Each group will get a set of different sizes clear containers.
3. Teacher will pour different volumes of water into each container as shown in Picture A..
4. Students are asked to compare the volume of water in the containers and arrange the containers
in ascending order according to the volume of water in the containers.
Expected answer : B, C, A, Din ascending order according to the volume of water in the containers.
5. Students will work in their group and pour the water of the containers into the beakers marked
A,B,C and D.
A,B,C and D.
6. Students arrange the beakers in ascending order according to the level of water in the containers.
7. Ask the students to compare the answers the have found in step 4 and 6.
Expected answer : D, B, A, C
8. Guide the students to tell that the tallest cup not always holds more, because of the way
they are displayed.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
they are displayed.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Worksheet
Name : ___________________________ Date :
Year 2 ____
Cicle the bigger container.
High achiever students
Activity 2
Learning Outcome:
- To compare volumes of liquid.
- To measure the volumes of liquid.
Materials:
- 500ml graduated beakers
- Various clear containers of different sizes
- A large pail of water
Procedures:
1. Divide the class into five groups. 2. Each group will get a set of different sizes-of clear containers.
3. Teacher will pour different volumes of water into each container.
4. Students are asked to compare the volume of water in the containers and arrange the
containers in ascending order according to the volume of water in the containers.
Expected answer : B, C, A, Dcontainers in ascending order according to the volume of water in the containers.
5. Student will work in their group and pour the water of the containers into the beakers marked
A,B,C and D.
6. Read the measurements of the beakers and fill in their findings in the following table: A,B,C and D.
Container | A | B | C | D |
Volume (ml) | 300ml | 230ml | 350ml | 180ml |
7. Students arrange the beakers in ascending order according to the level of water in the containers.
8. Ask the students to compare the answers the have found in step 4 and 6.
9. Ask the students to categorize the beakers into two groups with two beakers in a group that
hold the same volumeof water.
hold the same volumeof water.
Group A : Beaker A and beaker B (300ml +230ml =530ml)
Group B : Beaker C and beaker D (350ml + 180ml = 530ml)
10. Pupils pour coloured-water from the beakers in a group into another beaker to check their answers.
10. Pupils pour coloured-water from the beakers in a group into another beaker to check their answers.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Worksheet
Name : ___________________________ Date :
Year 2 ____
Fill in the blanks with the correct answers.
 |
1) The total volume of water in measuring cylinder A and C is _________
2) Measuring cylinder B holds __________ ml water more than measuring cylinder A.
3) Measuring cylinder C holds __________ ml water less than measuring cylinder B.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Conclusion
The most effective method of eliminating math misconceptions is to address them immediately when observed. This is imperative, so students do not carry these misconceptions any further and develop a better understanding of mathematics. When students have the opportunities to carry out activities or experiments on comparing the volume of water in the containers, they will realized that the volume of water in a container is not based on the height of water in the container or the shape of the containers. By using direct comparisons and hands-on activities,students will be able to correct this misconception because this misconception is caused by visual perception.References
- Irwan Rouf, Yayan Sopyan (2008): Cara Mudah Membina Laman Blog. Kuala Lumpur. Synergr MediaSdn. Bhd.
- Mok Soon Sang. (2004): A Primary Education Course In Mathematics for Post Graduate Diploma (K.P.L.I). Selangor. Kumpulan Budiman Sdn.Bhd.
- Murugiah s/o Velayutham & Kao Thuan Keat (2010): HBMT2103 Teaching Mathematics In Year Two. Selangor. Meteor Doc. Sdn. Bhd.
- Rabiatol Adawiyah Bt Hashim, Yap Poh Moi, Cho Kin Tong (2003): Mathematics Year 2 Part 2 (Textbook). Selangor. Multi Media Synergy Corporation Berhad.








No comments:
Post a Comment